학업관리 세컨더리 9학년 과학 - Science 9 소개
페이지 정보
본문
캐나다 세컨더리 9학년에 배우는 통합과학 Science 9 과목에 대해 간략히 설명하도록 하겠습니다. BC Science 9 과목은 9학년이라면 반드시 이수해야 하는 필수 과목으로 물리, 화학, 생물, 지구과학 4개 영역의 핵심과 기본적인 사항을 배우게 됩니다.
생물 Biology
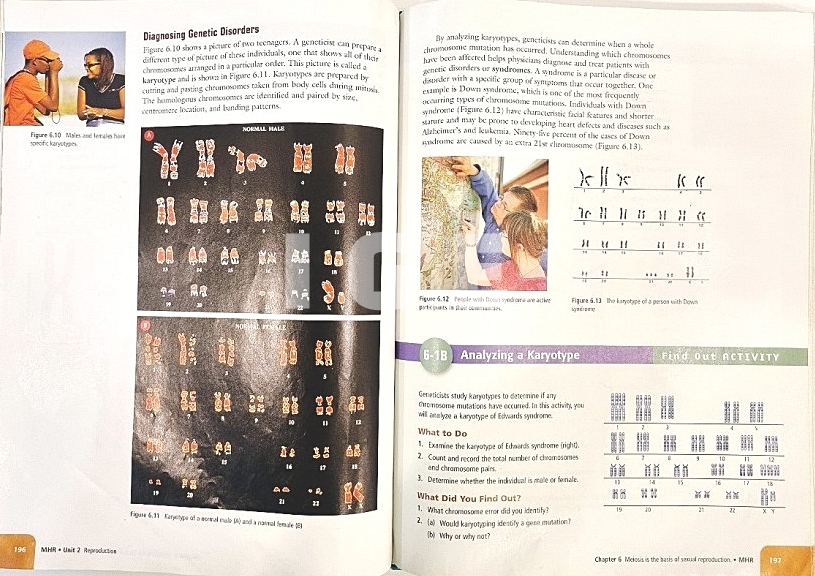
A. 세포 생식
(Cellular Reproduction)
1. 세포의 생식이 왜 중요한가?
(Why is the reproduction of cells Important?)
- 생식은 생명이 현세대를 넘어서 존재함을 보장한다.
(Reproduction ensures that life exists beyond its present generation.)
- 생식은 윗세대에서 아랫세대로 유전 정보를 전달한다.
(Reproduction transfers genetic information from parents to offspring.)
2. 왜 생물이 무성생식을 하는 방법이 각기 다른가?
(Why are different ways that living things reproduce asexually?)
- 박테리아는 이분열을 통해 생식한다.
(Bacteria reproduce by binary fission.)
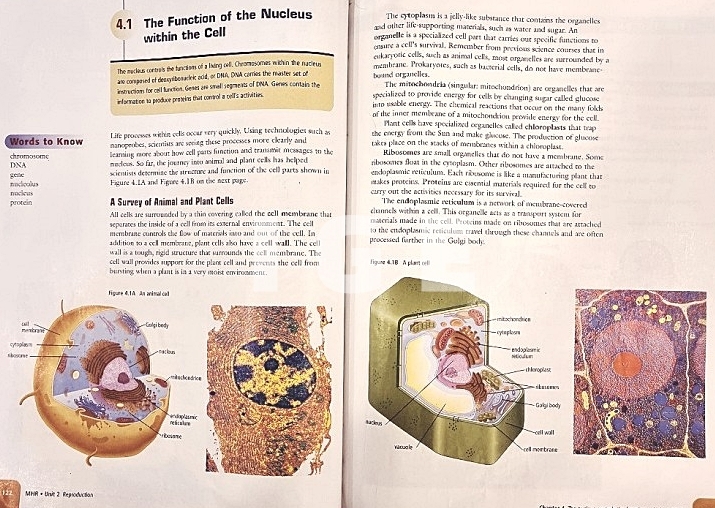
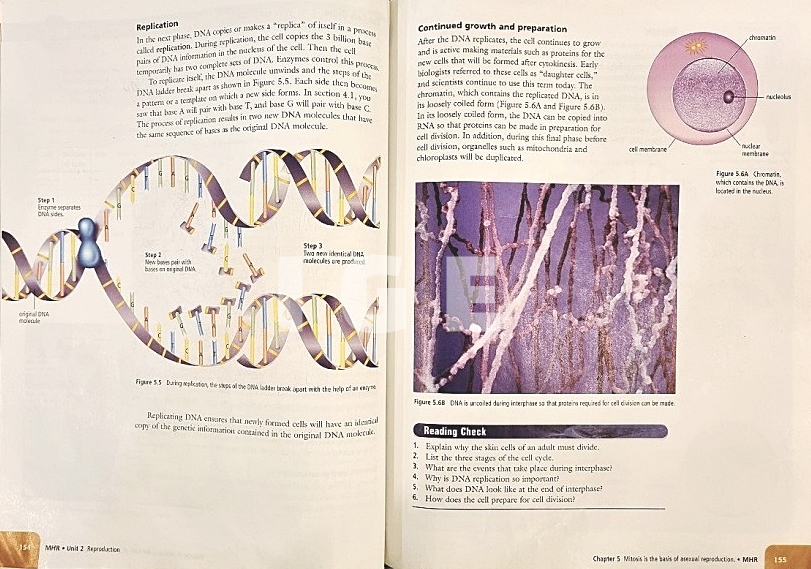
- 모든 진핵 세포는 세포주기를 통해 생식한다.
(All eukaryotic cells reproduce by the cell cycle.)
- 효모는 출아법을 통해 생식한다.
(Yeasts reproduce by budding.)
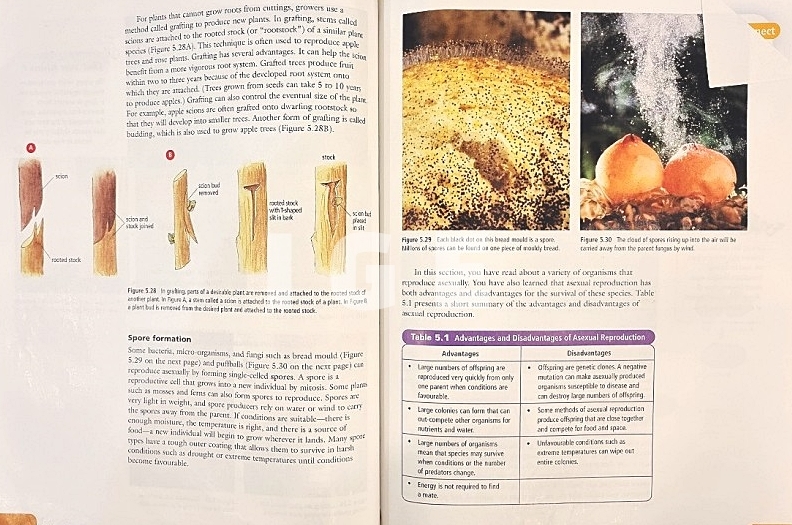
- 곰팡이는 포자법을 통해 생식한다.
(Moulds reproduce using spores.)
- 식물은 다양한 방법으로 무성생식을 한다.
(Plants have many ways to reproduce asexually.)
3. 생물은 어떻게 유성생식을 하나?
(How do living things sexually reproduce?)
- 수컷과 암컷의 생식세포가 결합해 접합자를 만든다.
(Male and female reproductive cells combine to produce a zygote.)
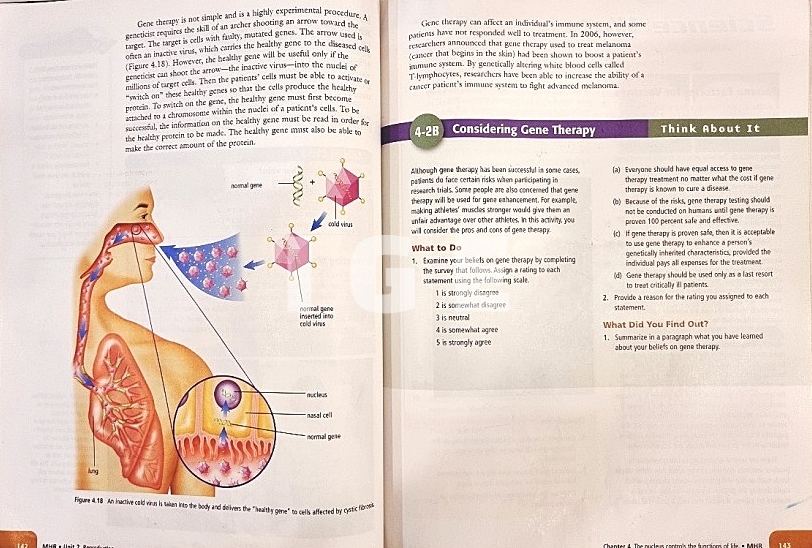
- 생식세포는 감수분열이라고 불리는 세포 분열 과정에 의해 형성된다.
(Reproductive cells are formed by a cell-dividing process called meiosis.)
- 인간 접합자의 발달은 단계적으로 일어난다.
(Development of the human zygote occurs in stages.)
- 유성생식은 다양한 형태를 띈다.
(Sexual reproduction takes many different forms.)
4. 생식이 지구상의 다양한 생명체에 어떻게 기여하는가?
(How does reproduction contribute to the variety of life on Earth?)
- 무성생식은 짧은 시간 안에 유전적으로 동일하게 많은 자손을 낳는다.
(Asexual reproduction results in many genetically identical offspring in a short amount of time.)
- 유성생식은 유전적으로 다양하게 자손을 낳는다.
(Sexual reproduction results in genetically varied offspring.)

화학 Chemistry
B. 원자론
(Atomic Theory)
1. 우리는 어떻게 그리고 왜 물질을 탐구하는가?
(How and why do we study matter?)
- 물질과 물질간 상호작용은 우리의 세계를 구성한다.
(Matter and its interactions make up our world.)
- 물질을 다룰 때는 안전이 매우 중요하다.
(Safety is key when working with matter.)
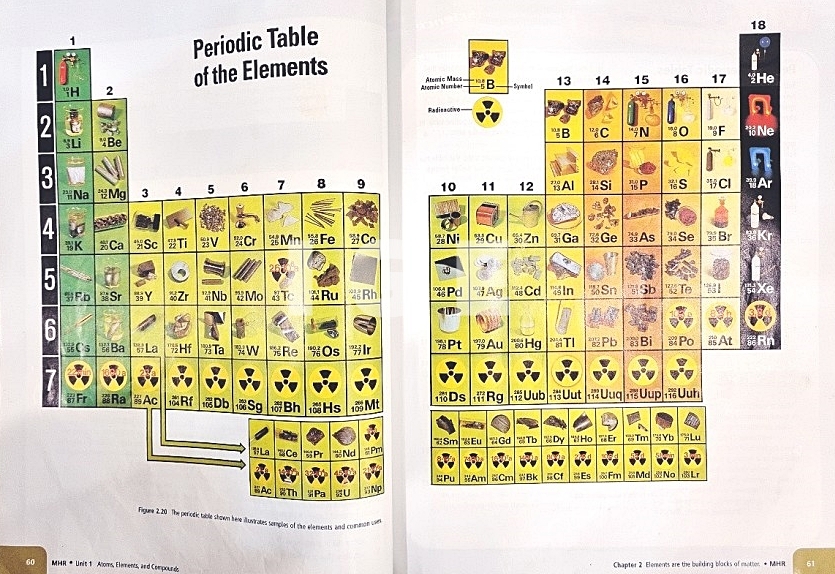
2. 주기율표는 어떻게 원소를 분류하나?
(How does the periodic table organize the elements?)
- 원소는 물질의 구성 요소이다.
(Elements are the building blocks of matter.)
- 원소는 각각의 화학적 특성에 따라 분류된다.
(Elements can be organized by their properties.)
- 현대의 주기율표는 원소를 주기와 족으로 분류한다.
(The modern periodic table organizes elements in groups and periods.)
- 원소는 금속, 비금속, 반금속 등으로 분류된다.
(Elements are classified as metals, non-metals, or semi-metals.)
3. 원자론은 주기율표의 패턴을 어떻게 설명할 수 있는가?
(How can atomic theory explain patterns in the periodic table?)
- 원자의 구조는 간단한 도표로 나타낼 수 있다.
(The structure of atoms can be represented using simple diagrams.)
- 화학적 그룹의 원소들은 비슷한 전자 배열을 가지고 있다.
(Elements in chemical groups have similar electron arrangements.)
- 주기율표는 원소의 성질이 예측 가능한 방식으로 어떻게 변화하는지 보여준다.
(The periodic table shows how properties of elements change in predictable ways.)
4. 어떻게 원소들이 결합하여 화합물을 만드는가?
(How do elements combine to form compounds?)
- 화합물은 지구상의 매우 다양한 물질들을 설명한다.
(Compounds account for the huge variety of matter on Earth.)
- 이온 화합물은 이온으로 이루어져 있다.
(Ionic compounds are made of ions.)
- 공유 결합 화합물은 분자로 이루어져 있다.
(Covalent compounds are made of molecules.)
- 공유 결합은 원소와 그물형 고체에서도 발생한다.
(Covalent bonding also occurs in elements and network solids.)
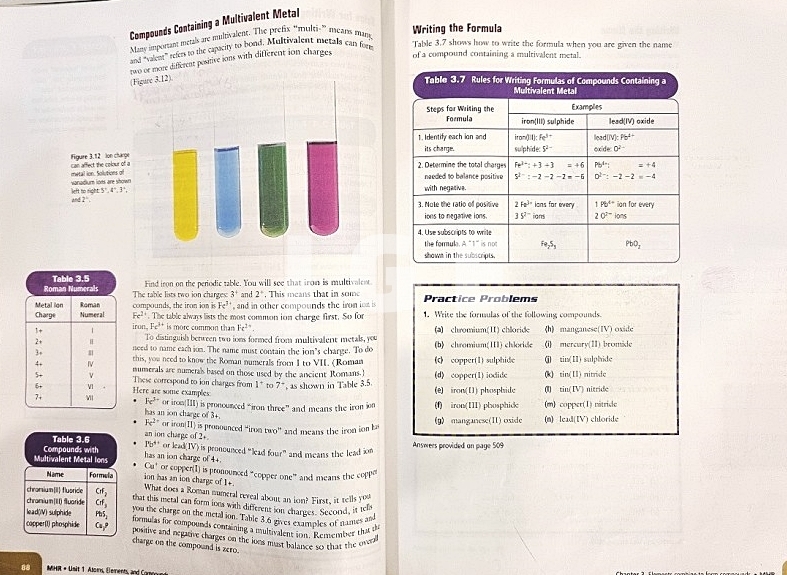
5. 화합물 명명법과 화학식
(How do we name and write formulas for compounds?)
- 이온 화합물의 화학명을 보면 그 구성 요소를 알 수 있다.
(The chemical name of an ionic compound communicates its composition.)
- 우리는 이온 화합물의 명칭을 통해 공식을 알아낼 수 있다.
(You can determine the formula of an ionic compound from its name.)
- 다가 금속은 하나 이상의 이온을 형성한다.
(Multivalent metals form more than one ion.)
- 다원자 이온은 하나 이상의 원자로 이루어져 있다.
(Polyatomic ions are made up of more than one atom.)


물리 Physics
C. 전기의 생산과 분배
(Production and Distribution of Electricity)
1. 전기 에너지가 어떻게 우리 세계의 일부를 구성하나?
(How is electrical energy part of your world?)
- 전기 에너지는 많은 응용분야가 있다.
(Electrical energy has many applications.)
- 다양하게 많은 종류의 에너지가 전기 에너지로 변환될 수있다.
(Many different types of energy can be transformed into electrical energy.)
- 전기 에너지는 여러 자원으로부터 다양한 방식으로 생성된다.
(Electrical energy is generated in different ways from different sources.)
2. 전하는 어떻게 활동하는가?
(How do electrical charges behave?)
- 전자는 음전하를 띠고, 양성자는 양전하를 띤다.
(Electrons carry a negative charge, and protons carry a positive charge.)
- 서로 다른 전하끼리는 끌어당기고 같은 전하끼리는 밀어낸다.
(Opposite charges attract each other, and like charges repel each other.)
3. 회로의 구성 요소를 통해 전하가 어떻게 이동하나?
(How do charges flow through the components of a circuit?)
- 화학 에너지는 전지의 전하를 분리한다.
(Chemical energy separates electrical charges in cells.)
- 전하는 도체를 통해 흐르지만 절연체는 흐를 수 없다.
(Charges can flow through conductors, but not insulators.)
- 움직이는 전하는 전류를 형성한다.
(Moving electrical charges form an electric current)
- 부하는 전류의 흐름에 저항한다.
(A load resists the flow of current.)
- 도체는 전류가 흐를 수 있도록 폐루프를 형성해야 한다.
(Conductors must form a closed loop to allow current to flow.)
4. 회로는 실제 응용 분야에서 어떻게 사용되는가?
(How are circuits used in practical applications?)
- 회로의 전압, 전류 및 저항은 옴의 법칙과 연관되어 있다.
(Voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit are related by Ohm's law.)
- 회로에서 부하를 직렬 또는 병렬로 연결할 수 있다.
(Loads can be connected in series or in parallel in a circuit.)
- 가정 내 회로는 병렬 부하가 실용적이다.
(Parallel loads are practical for circuits in the home.)
5. 어떻게 해야 전기 에너지를 지속적으로 생성하고 사용할 수 있는가?
(How can electrical energy be generated and used sustainably?)
- 지속 가능한 전기 에너지 사용은 전기 에너지 사용이 어떻게 측정되는지를 먼저 알아야 한다.
(Sustainable use of electrical energy begins with understanding how its use is measured.)
- 정보에 입각한 의사결정은 전기 에너지를 지속적으로 사용하는데 도움을 준다.
(Making informed choices helps you use electrical energy sustainably.)
- 재생 에너지 자원은 전기 에너지를 지속적으로 생성하기 위한 선택권을 제공한다.
(Renewable energy sources provide sustainable options for generating electrical energy.)






지구과학 Earth Science
D. 지구 시스템
(Earth's Major Spheres)
1. 지속가능성과 연관성 대한 방안들은 지구 시스템에 어떻게 도움이 되는가?
(How do the ideas of connections and sustainability help us think about Earth's spheres?)
- 우리는 모두 연결되어 있다.
(We are all connected.)
- 지속가능성은 현재와 미래를 위한 균형 잡힌 시스템을 보장한다.
(Sustainability ensures balanced systems now and for the future.)
- 과학 지식이 풍부한 시민들은 정보 출처에 대한 편견을 알고 있다.
(Scientifically literate citizens are aware of bias in sources of information.)
2. 지구 시스템에서 태양 에너지의 역할은 무엇인가?
(What is the role of the Sun's energy in Earth's spheres?)
- 지구에 도달하는 태양 에너지는 지구의 대기와 지표면에 흡수되고 반사된다.
(Solar energy that reaches Earth is absorbed and reflected by Earth's atmosphere and Earth's surface.)
- 태양 에너지는 지구의 지표면을 불균일하게 데우고, 지구의 바람은 지구의 열에너지를 재분배하도록 도와준다.
(Solar energy heats Earth's surface unevenly, and global winds help redistribute thermal energy around Earth.)
- 해류는 지구의 열에너지를 재분배한다.
(Ocean currents also redistribute thermal energy around Earth.)
- 태양 에너지는 광합성과 세포 호흡을 통해 생물권에 진입한다.
(Solar energy enters the biosphere through photosynthesis and cellular respiration.)
3. 어떠한 상호작용을 통해 지구 생물권에 에너지가 공급되는가?
(What interactions supply energy to Earth's biosphere?)
- 생산자는 소비자와 분해자에게 에너지를 전달한다.
(Producers transfer energy to consumers and decomposers.)
- 생물권을 유지하고 지속적인 에너지 흐름을 위해서는 상호작용이 필요하다.
(Interactions are needed to provide a constant flow of energy to sustain the biosphere.)
4. 어떠한 상호작용의 순환이 지구 시스템에 있어 중요한가?
(What interactions cycle matter through Earth's spheres?)
- 물의 순환은 태양 에너지와 중력에 의해 이뤄지는 연속적인 순환이다.
(The water cycle is a continuous cycle driven by solar energy and gravity.)
- 탄소는 생물과 무생물 사이의 상호작용을 통해 순환된다.
(Carbon is cycled through interactions between living and non-living things.)
- 질소는 생물과 무생물 사이의 상호작용을 통해 순환된다.
(Nitrogen is cycled through interactions between living and non-living things.)
- 인은 생물과 무생물 사이의 상호작용을 통해 순환된다.
(Phosphorus is cycled through interactions between living and non-living things.)
5. 우리의 행동이 어떻게 지속가능성을 높일 수 있을까?
(How can our actions promote sustainability?)
- 각각의 의사를 물어보는 것으로도 변화를 만들 수 있다.
(Inquiring individuals can make a difference.)
- 책임 있는 의사 결정과 선택이 모두에게 이로운 지속 가능한 실천으로 이끌 수 있다.
(Responsible decision making and choices can lead to sustainable practices that benefit all life.)
세컨더리 9학년 통합과학 Science 9 과목 학습 내용 한눈에 볼 수 있도록 표로 정리합니다.
9학년 통합과학(Science 9) | ||
단 원 | 내 용 | |
생물 | 1. 세포 생식의 중요성 | ▶개체 유지 ▶유전 정보 전달 |
2. 무성생식 | ▶이분열 ▶세포주기 ▶출아법 ▶포자법 | |
3. 유성생식 | ▶접합자 ▶감수분열 ▶인간의 접합자 발달 과정 ▶유성생식의 다양한 형태 | |
4. 무성생식과 유성생식의 차이 | ▶무성생식의 특징 ▶유성생식의 특징 | |
화학 | 1. 물질 탐구 | ▶우리 세계의 일부인 물질 ▶화학실 안전 규칙 |
2. 주기율표 | ▶원소 ▶화학적 특성에 따른 원소 분류 ▶주기율표 분류법 ▶원소의 종류 | |
3. 원자론과 주기율표 패턴 | ▶도표로 보는 원자 구조 ▶화학적 그룹의 원소들 특징 ▶원소의 성질 변화 | |
4. 화합물 | ▶화합물 설명 ▶이온 화합물 ▶공유 결합 화합물 ▶공유 결합 | |
5. 화합물 명명법과 화학식 | ▶이온 화합물의 화학명과 공식 ▶다가 금속 ▶다원자 이온 | |
물리 | 1. 전기 에너지 | ▶전기 에너지의 활용분야 ▶전기 에너지 전환 ▶전기 에너지 생성 |
2. 전하 | ▶전자와 양성자 ▶전하의 성질 | |
3. 회로 | ▶화학 에너지 ▶도체와 절연체 ▶전류 ▶부하와 저항 ▶폐루프 | |
4. 회로의 실제 응용 분야 | ▶옴의 법칙 ▶직렬회로와 병렬회로 ▶병렬 부하의 실용성 | |
5. 지속 가능한 전기 에너지 사용 | ▶전기 에너지 사용 측정 방법 ▶정보에 입각한 효율적인 의사결정 ▶재생 에너지 자원 활용 | |
지구 과학 | 1. 지구시스템 | ▶지속가능성과 연관성 ▶균형 잡힌 시스템을 위한 노력 ▶풍부한 과학 지식 |
2. 태양 에너지 | ▶태양 에너지의 흡수와 반사 ▶대기류를 통한 열에너지 재분배 ▶해류를 통한 열에너지 재분배 ▶태양 에너지와 생물권 관계 | |
3. 지구 생물권 | ▶생물을 통한 에너지 전달 과정 ▶생물권의 상호작용 | |
4. 상호작용의 중요성 | ▶물의 순환 ▶탄소의 순환 ▶질소의 순환 ▶인의 순환 | |
5. 지속가능성을 높이기 위한 노력 | ▶개개인의 노력 ▶책임 있는 의사 결정과 선택 | |
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.


회원가입/로그인 후 댓글 남겨 주세요.
로그인/회원가입